
Decentralization is a pillar of the blockchain ethos, and Ethereum developers are currently prioritizing new features that take this principle to the next level.
That’s called Distributed Validator Technology, or DVT.
Decentralize validators
The Ethereum blockchain relies on hundreds of thousands of validators to approve transactions that take place on the network, and each validator can be seen as a point of failure.
Additionally, validators themselves can face severe financial penalties, known as “thrashing,” if they are offline for a period of time. Validators also have incentives to increase their own resilience.
So the idea of decentralizing the validators themselves emerged.
Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin has tweeted a revised roadmap for Ethereum to celebrate Beacon Chain’s one year anniversary, making decentralized validators one of his top priorities, at least beyond 2021. is listed.
Happy birthday beacon chain!
Here’s an updated roadmap diagram for where Ethereum protocol development is at and what’s coming in what order.
(I’m sure this is missing a lot, as all diagrams are, but it covers a lot of the important stuff!) pic.twitter.com/puWP7hwDlx
— vitalik.eth (@Vitalik Buterin) December 2, 2021
“Happy Birthday, Beacon Chain!
This is a revised roadmap showing the current and future development of the Ethereum protocol.
(Like any diagram, I think there’s a lot that’s missing in this roadmap, but it covers a lot of the important points.)
DTV has recently been working with entrepreneurs and cryptocurrencies such as Messari, Coin Metrics, Bankless, Wu Blockchain and Pantera Capital. ) has been actively discussed among analysts and has become the focus of development.
Last milestone of current phase
With DVT, validator private keys used for signing on-chain activities such as block proposals and authentications can be distributed across multiple node operators. As a result, the role of validator can be distributed and shared across a cluster of node operators rather than a single node.
Decentralized validator technology “allows multiple people to run a single validator,” said Steven Quinn, head of research at staking service P2P. From a physical point of view, it means that machines can be distributed geographically.”
The aforementioned roadmap, which was announced in 2021, is not exhaustive, but it shows the trajectory of Ethereum so far and in the future, and depicts various phases of its current and future development.
Although the Ethereum blockchain has successfully transitioned to a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism and completely overhauled its system of transaction processing, it is currently still in its first phase called “The Merge”.
One of the major milestones left in the current phase is the deployment of decentralized validators, which is progressing thanks to two open source networks, Obol and SSV.
Advantages of DVT
As stated on its official website, the Obol network is “responsible for promoting multi-operator validation as a use case for decentralized validator technology.”
The SSV network “enables decentralized operation of Ethereum validators across different operators.”
Each Ethereum validator currently runs on a single node, which Obol and SSV see as a single point of failure in the validation process.
If a node operator goes offline and becomes unavailable due to infrastructure bugs in the validator’s client software, the validator will not be able to perform its duties such as proposing and validating blocks.
As a result, validators will be penalized for staked Ethereum (ETH), known as thrashing. Obol and SSV seek to remove this single point of failure in the validation process.
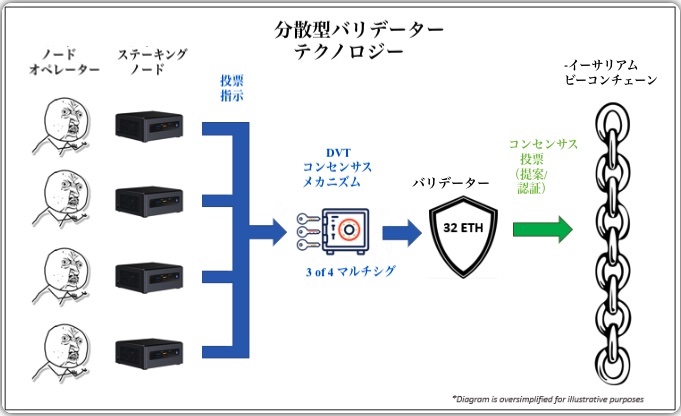
 Configuration that requires 3 out of 4 node operators to cast validator votes (leoglisic.eth)
Configuration that requires 3 out of 4 node operators to cast validator votes (leoglisic.eth)Regarding DVT, Messari Research Analyst Stephanie Dunbar said, “What excites me the most is increased resilience on Ethereum and, in the future, on other blockchains.” .
The importance of DVT is to make the Ethereum blockchain even more resilient. That is defined as Ethereum being “able to withstand geopolitical, regulatory, market, external and internal failures such as fires and earthquakes,” said Walter Smith of investment firm Galaxy. Told.
With more clients and node operators running as a single validator in different geographic areas, even if multiple node operators experience downtime due to criminals or codebase bugs, If most of the network leverages decentralized validator technology, the whole validator will not go down.
“Even if less than 33% of the nodes participating in the DV cluster go offline, the remaining active nodes can still form consensus on what to sign and produce valid signatures for staking missions. explains Obol.
Decentralized validator technology is the last major development of ‘The Merge’ phase before moving to ‘The Surge’, Obol and SSV gearing up to bring decentralized validators to Ethereum mainnet tidy up.
SSV is in the final stages before its mainnet launch, and introduced a public testnet called Jato in March. Obol began deploying decentralized validators on the Ethereum mainnet in April.
DVT will “make the heart of the cryptocurrency universe, Ethereum, more robust, decentralized, trustworthy and neutral, and more stable and open to all with its protocols and use cases.” Mr Smith said.
|Translation and editing: Akiko Yamaguchi, Takayuki Masuda
|Image: Shutterstock
|Original: ‘Distributed Validator Technology’ Marks Last Key Milestone in Ethereum’s Current Era
The post Ethereum, the final milestone of the current phase “Decentralized Validator Technology” | CoinDesk JAPAN | CoinDesk Japan appeared first on Our Bitcoin News.

 2 years ago
190
2 years ago
190














 English (US) ·
English (US) ·