Editor’s note: Jenny Lefcourt is a TechCrunch Live guest on August 31, 2022 where, along with Guillaume de Zwirek, CEO and co-founder of WELL Health, she’s scheduled to speak on the specific steps founders should follow when raising a Series A. The event records live and is available to watch at 12:00pm PDT. It’s free to attend. Register here. Replays will be available and posted here following the event.
Beginning with the first company I co-founded 25 years ago and continuing through the second company I co-founded 15 years ago, I raised over $100M from top-tier VCs. During that time, less capital was floating around, and those numbers were considered enormous. The bad news is that I over-capitalized my companies, but the good news is that the process taught me how VCs think and the best way to pitch them. Since 2014, I’ve been a seed-stage investor at Freestyle and had the opportunity to fine-tune this skill by working closely with founders in our portfolio on raising Series A rounds. The market is demanding right now – founders, I hope the following guide helps many of you fundraise in this challenging environment.
The key when raising is to understand what VCs are looking for in a founder and a business at each stage, and then you can make the call on the best way to pitch them in a way that feels right to you.
There’s a notable difference between raising Seed and Series A rounds: A Seed is often raised solely on a founder’s big vision, whereas a Series A typically needs a big vision and business traction, especially in the current market. Below are general best practices for pitching, followed by specific advice on structuring a Series A story arc.
Fundraising wisdom for any stage
- Mindset matters! Enter a meeting with the spirit of having an intellectual conversation about your business v being in hard-core “sell” mode. VCs prefer to work with founders who can discuss their business thoughtfully. Be curious, confident, and ready to debate–and, at all costs, resist being defensive. I discuss mindset more here, Learn to Love Fundraising.
- Trust is table stakes. If you don’t know the answer to a question, saying so gains respect and trust, while avoiding the question destroys it. One of the easiest ways to lose an investor’s interest in a first meeting is for the VC to feel like you aren’t being direct. There’s no expectation of you knowing all the answers–there is an expectation of telling it straight.
- VCs have short attention spans! You need to get them interested in the first 5-10 minutes of the meeting to earn their attention for the rest. See more below on “Section 1.”
- Goal of meeting #1 is to get meeting #2. Your goal is not to tell them everything or pre-emptively answer any question they may ask. So keep your story high level and interesting – do not data dump or mire them in the details too early.
- Tell a good story vs. “present slides”. This is why I recommend that founders spend time crafting their story arc, followed by creating the slides to support that story.
Make your main points very clear and support those points with the data or color that helps them believe. Don’t make VCs listen to a lot of talk and inundate them with a lot of data in hopes that they connect the dots. Subtle does not win here. - Prepare for questions. Have a hearty appendix that covers any question you may get or does a deeper dive into the business. VCs love it when they ask a question and the founder pulls up a slide that directly addresses it. The VCs get the information they are looking for, and you show them that you are just the kind of thoughtful founder with whom they like to work!
Manage time. Know how much time you have and make sure to make your main key points. Don’t let it get to minute 30, and you’re still down a rabbit hole on a non-critical part of the business.
Series A Fundraising wisdom
When your first Series A pitch is over, ideally, the VC is excited about the opportunity, impressed with you, knows enough to believe you are on a promising path, and is still thinking about you and your business well after the meeting. Typically founders have 30 minutes (often over Zoom) to make this happen.
I recommend thinking about your pitch in three “Sections.”
SECTION 1: The goal is to earn the right to their attention for the rest of the meeting! It may include some/all of the following:
- Team
- Vision. The big vision of the company–NOT simply what you do today.
- Market. Educate VCs about your market, which includes market size and macro trends. VCs should understand that it is a big market and understand a reason for the “why now?” question.
- Problem/Opportunity. Make it clear who your customer is and what their problem is that you are solving. Sometimes it is less of a “problem” you are solving and more of a new opportunity that now exists, given the changes in the market.
- Solution for stated problem/opportunity (precisely what your company does!)
- Early sign of success. Have a visual here where you can imagine the title of this slide being “And it is Working!” This may be a graph of a key metric like revenue or users that goes up and to the right, lots of logos of companies that have already signed up, or other goodness. The goal here is to get them leaning in and excited to learn more.
After pitching this section, take a breath and check in with the investors. Ask: “Any questions? Does this sense?”
SECTION 2: The goal here is to educate them on how you have de-risked the business thus far and presented traction on product and growth. This section typically contains some or all of the following:
- Where you have started. Note: all startups have to start somewhere. You told them earlier what the big vision is. Now you want to tell them where you started (and maybe why) and how it is going. Just be careful not to get bogged down in too much detail.
- Your customers. Who they are and what your value proposition is for them.
- Go to Market. Explain how you target/acquire customers.
- Traction thus far. You want to be clear about the main levers/metrics that drive your business and share information on how those have evolved. You do not need to cover all metrics and details–you can cover that in the Appendix. Here is a laundry list of potential traction metrics: new customers/total customers, retention/churn, engagement, sales funnel conversion, sales pipeline, average sales price, revenue, gross margins, CAC payback, LTV:CAC ratio,…
- Unit Economics
- Product Love. Ideally, you share engagement stats or something that shows that people are not just buying/using your product but are loving it and finding it indispensable. Possibilities here include engagement stats, virality, spending more time or money with your business over time, putting more of their business on your platform, etc. A few testimonials alongside the data can also help.
- Any other slide that is CRITICAL to your company’s success.
- Competitive landscape. This is NOT a feature comparison but rather a market mapping to educate them on the players. Many use a 2×2 map to show who is in the market based on two attributes where your company sits alone in the top right quadrant. This may feel counter-intuitive, but you want big, important players on this map as you want your prize to be worth winning. Example from Scenery:
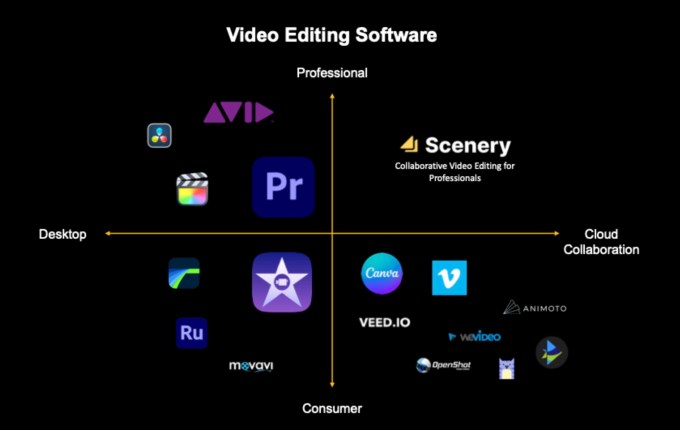
A screenshot from Scenery’s pitch deck
SECTION 3: The goal here is to tell a straightforward story of where you are headed from here and how the business becomes massive. This section typically contains some or all of the following:
- Product and/or strategic/geo rollout roadmap. Cover your plans and explain why you believe this is the best path forward
- 3-year financial projections (maybe here, maybe Appendix)
- Milestones you will hit with this round. Note: most VCs care less about how you will “spend” the capital than what you will achieve with the capital (note: use of proceeds can be a good Appendix slide.). VCs want your business to be more valuable by the time you raise your next round. Potential milestones could include revenue, number of users, product/technology developed, number of markets you will be in, and key partnerships,…
APPENDIX: The goal here is to address any question you may get asked or dive deeper into an aspect of your business. As you get more questions, add more appendix slides! I recommend pulling a specific slide up when asked for more information on a subject. Some potential appendix slides include:
- Sales productivity
- Sales pipeline
- Deeper dive into current customers
- Acquisition and payback period by channel
- Deeper breakdown of market
- Cohort analysis
- Net Promoter Score (NPS) or Sean Ellis test
- Product Roadmap
- Geography rollout plans
- Organization structure and team + key hires
Unquestionably, fundraising can be daunting and exhausting. However, I would encourage you to recognize some positive aspects of fundraising…the clarity you gain about your business as you prepare to pitch, the wisdom you will get from many of your meetings and something not discussed as much, the customers you can acquire when interested VCs introduce you to their portfolio companies. Lastly, remember, you only need one VC to say yes!
A couple of additional resources:
If you’ve yet to raise your Seed round, you may find this interesting to watch (especially for women founders). Jess Lee @ Sequoia and I dissected a VC pitch for Seed for All Raise’s first Female Founder Office Hours.
Top-tier pitch agency, 4th & King, and I did a session on Series A Fundraising with Freestyle portfolio founders, which you can watch here.













 English (US) ·
English (US) ·