Belgian startup Telraam designed a device that lets anyone point out of a window a camera-like device that uses on-board tech to count the number of road users. It is currently installing a network of 50 or so devices in San Francisco, a project the company says is largely funded by Yelp CEO Jeremy Stoppelman, with support of “local civic groups such as SF Parks Alliance and the Slow Streets Mayors.”
Telraam (the name is Dutch and means “counting window”) claims its tech is particularly useful for “addressing social issues” and “creating valuable citizen engagement for transport authorities and urban planners.” Traffic monitoring has been on the minds of urban planners and traffic wonks for a long time — TechCrunch published an impassioned plea for better data back in 2015, for example.
“The pilot will demonstrate the quality of data that can be gathered in partnership with community groups to the SFMTA, saving them money and time, adding a greater level of detail than was available previously, and creating new channels of engagement with the residents involved,” says Telraam’s CEO Kris Vanherle. “If these 50 devices can demonstrate that Slow Streets are, or are not, performing as expected, and which ones and what interventions are most successful, then both the counting network and the Slow Street networks can be expanded.”
The San Francisco project represents the first deployment of the company’s products outside of Europe — existing cities that are sensored up are Utrecht, Amsterdam, Berlin and Brussels. London is next.
The company says city planners need traffic data, but that the problem it is addressing has historically focused solely on motorized vehicle data on major roads. This is a challenge, because, of course, the urban traffic landscape is about more than cars, buses and the odd police car. By adding a focus on “livable urban streets,” the sensors also track walkers, bikers and other modes of transport.
The device is a camera sensor that detects moving objects from a residential window facing the street. It identifies the objects using machine learning and AI, then categorizes it along with the direction of travel and the speed (for vehicles). The anonymized data is then sent to Telraam servers. This creates an open data resource that is available to the device user on a dashboard but also to local network clients who monitor the devices in a particular area or region. From there, it’s made public via the company’s website map and API.
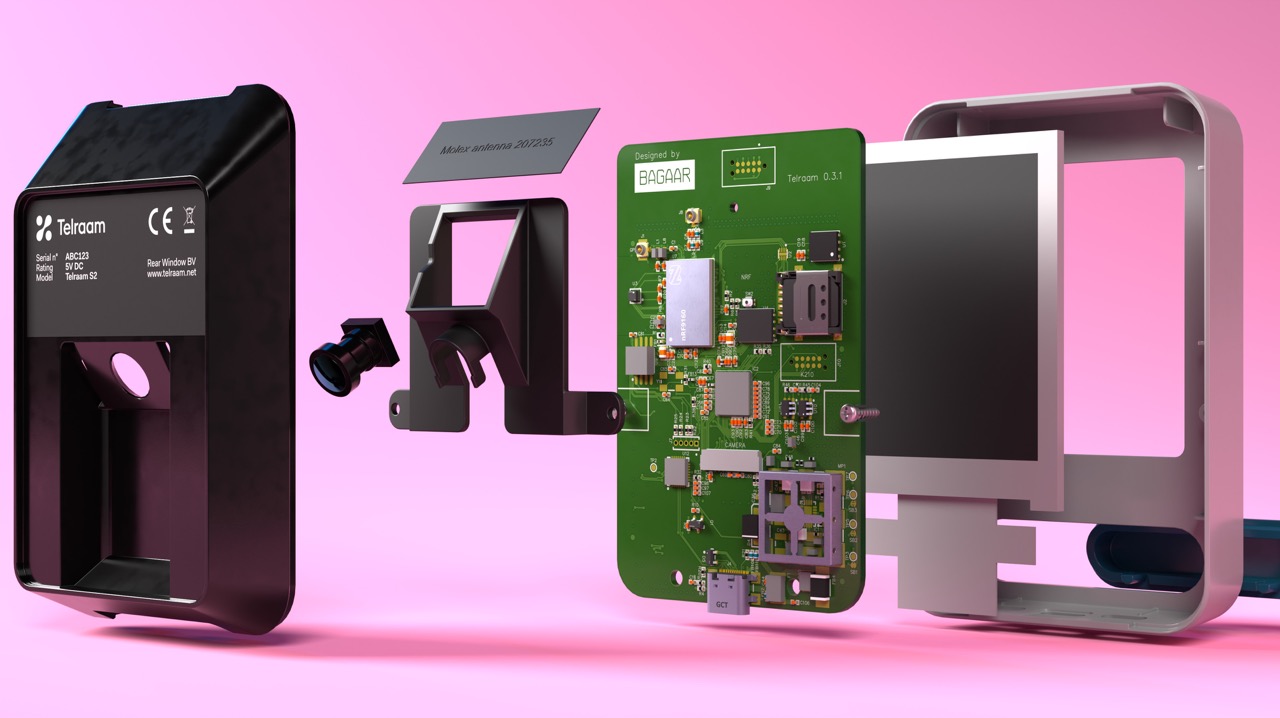

Gotta love a good exploded-product diagram. Image Credits: Telraam.
Privacy by design
As you might expect from a company based in Europe, which is becoming increasingly privacy-forward, Telraam has designed the device to be as private as possible. The low-resolution video images are processed on the device itself, then discarded, and the company says only the anonymized data table is transmitted off-device.
“The camera is deliberately low resolution. The quality is sufficient for the AI chip to process in order to recognize the moving objects and categorize them as a car, bike or pedestrian, for example, but not enough detail to be able to see a face or read a license plate. There is no chance to identify individuals or vehicles,” says Vanherle. “This means that Telraam S2 devices can provide useful traffic counts, but not collect any private information on the street users who pass by.”
You can check out the company’s traffic map yourself on the company’s website, and more industrial users can apply to gain access to an API to analyze the data in more detail.
“Individual campaigners can purchase a device for their own window and monitor their street, and use this to lobby their neighbors and local community for change. Ultimately they can also encourage whoever makes policy or planning decisions locally to gather more data together, and collaborate on local improvements,” Vanherle explains. “Telraam also works with local authorities to help organize and coordinate local networks that can be from 10 to 300+ devices depending on the requirements, and then to support them as they recruit local volunteers.”
This European startup is installing 50 traffic-counting sensors across San Francisco by Haje Jan Kamps originally published on TechCrunch













 English (US) ·
English (US) ·