Twenty years ago, getting a human genome sequenced was a billion-dollar, international project. Today, you can get your dog’s genome sequenced by the end of the month for a few bucks. It speaks to the speed with which genetics has permeated our lives, but despite massive improvements to the technology, the process can still be a bit clunky in the lab.
Before you can even start to disentangle someone’s genetic code, you have to start with a sample. And that sample has to get prepped the right way. It’s a relatively boring process that is often sidelined in favor of flashier applications of genome sequencing (read: reviving mammoths). But it’s a place where Volta Labs is aiming to bring a new focus.
Founded in 2018, Volta Labs is a startup spun out of MIT’s media lab focusing on creating a programmable approach to DNA sample prep. The team is in the process of creating a desktop-sized instrument that can automate the processes used to get genetic samples ready.
“The entire world could not sequence a single human genome 20 years ago, and today, I as a non biologist can sequence a human genome in a day or two on a bench. But if you look at the steps for sample prep, it’s still lagging by a large margin. It’s almost been neglected,” CEO and co-founder Udayan Umapathi told TechCrunch.
The origin story of Volta’s instrument goes back to 2015, when Umapathi was working on his graduate thesis at MIT. “What I noticed was that the existing technologies for moving, mixing and heating fluids were archaic,” he said. “I realized if we have to do biology at scale, automation for biology has to be built from the ground up.”
The DNA sample prep process starts with a biological sample, like blood, saliva or even plant tissue. From there, a series of enzymatic and chemical reactions are performed that draw out DNA molecules. Then they need to be manipulated so they can then be “read” by a sequencer. Those reactions are performed by liquid manipulating robots, or in some cases by hand.
Volta automates this process with what Umapathi called “digital fluidics” — a form of electrowetting. This uses an array of electrodes organized on a grid, each of which can be charged or discharged, creating something like a maze that can precisely position drops of liquid.
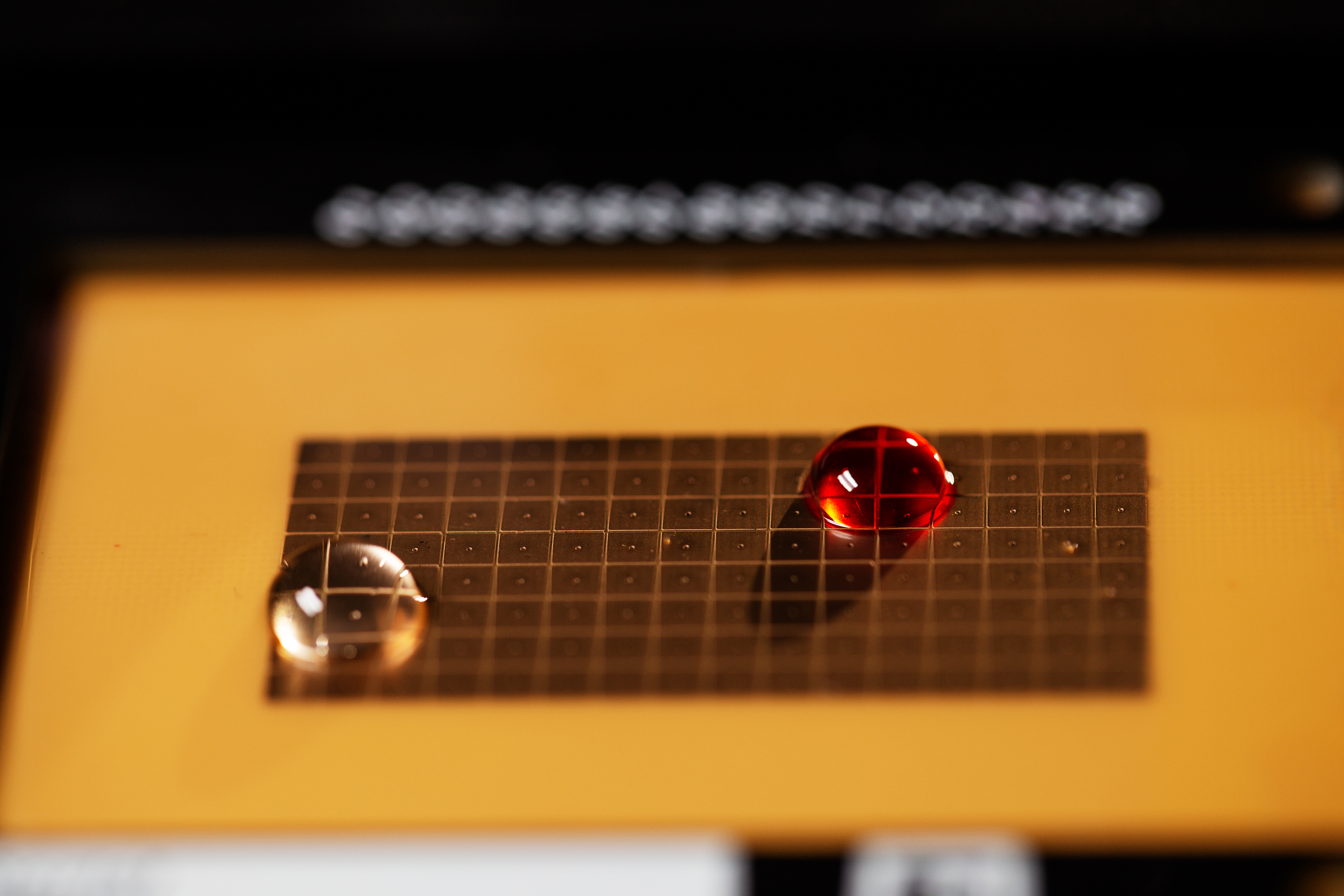
Volta’s digital fluidics array. Image Credits: Volta Labs
With the right programming, Umapathi is confident his platform allows liquids to be manipulated in even more complex ways, like using magnetic fields to draw certain molecules out of samples for further analysis.
Despite these capabilities, the instrument is supposed to be small: Umapathi’s goal is to keep it the size of a laptop.
Umapathi isn’t the first to see the potential that “digital fluidics” hold for biological applications. In fact, Illumina has been interested in technology of this nature for years.
In 2013, Illumina acquired Advanced Liquid Logic, a company founded in 2004 that had already been working on applying digital microfluidics to prep work for Next Generation DNA sequencing. In 2015, Illumina went on to try to launch its own version of a DNA library sample prep product called NeoPrep, which rolled the four to five day process into one instrument that could accomplish the task in 30 minutes. However, as the authors of a 2020 review paper on the electrowetting industry note, the instrument was “discontinued for undisclosed reasons” in 2017.
Whether the end of NeoPrep in 2017 has bigger implications for Volta’s own commercialization process is hard to say. But, it does seem that Illumina hasn’t put the idea to bed yet.
On Thursday, Volta announced a $20 million Series A round, which was led by Maverick Ventures (Maverick also led a previous seed round), with participation from Khosla Ventures, Casdin Capital and E14 Funds. Participants also include Illumina co-founder John Stuelpnagel, and other big names in the genetics space like Anne Wojcicki, CEO of 23andMe, and Paul McEwan, founder of Kapa Biosystems. McEwan specifically has led sequencing sample prep programs at Roche Sequencing Solutions.
The natural question here is: Does Volta’s instrument actually exist yet? It does, Umapathi said, and it is already in the hands of four partners that are testing it in the field. He declined to name the partners but described them briefly.
One is a company focusing on cancer care and neurological disorders, which has been using Volta’s tech to develop a DNA extraction process. One is a research institution in RNA applications. The third is a “genome center,” he says. The fourth company is a biotech firm interested in synthetic biology.
The company’s goal is to launch a “limited trial edition” at the AGBT Genomics conference in June. During that launch, Umapathi also expects to present data from the trial projects run with the “genome center.” He expects to have a commercial product ready in 2023.
The rapidly accelerating genomics industry may have room for Volta to climb on board. It cost $3 billion to sequence the human genome as part of the Human Genome Project. Today, that same process can be repeated for about $600. McKinsey’s 2020 genetics industry analysis estimated that the cost of genome sequencing could dip below $100 within a decade.
Amidst this background, the sample prep bottleneck seems obvious. The bigger question here is: Why haven’t the giants in genome sequencing already created the solution?
Part of the answer is that they’ve already tried, and some places, like Roche do have instruments that will address each little piece of the sequencing prep puzzle individually, as opposed to the integrated system Umapathi aims to create. But the answer Umapathi prefers is that existing sequencing technology is already complicated enough to be a full-time job.
“The technology we have built today is almost as complex as the sample prep itself. So for a lot of the sequencing tech companies, getting their core technology was already a massive challenge.”
Going forward, Volta has to prove that relatively complex chemistries can be manipulated inside such a compact instrument. It will have to publish far more data than it has right now to truly prove it can fit into this niche. Confidential trials with four customers and unpublished data aren’t enough.
But if it actually works, Volta may join the rise of an industry that’s already booming. With this Series A round, Umapathi plans to outline a manufacturing plan, and start to build out commercialization capacity.
“I think the big chunk of capital is likely going to go into building out a product strategy and commercialization or team as well as we approach commercialization next year,” he said.













 English (US) ·
English (US) ·