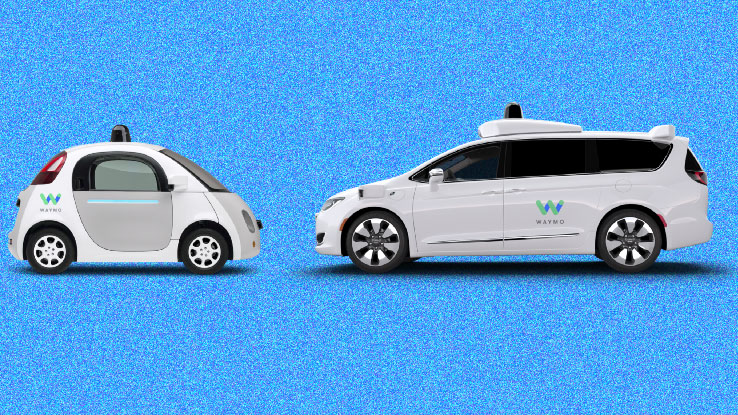
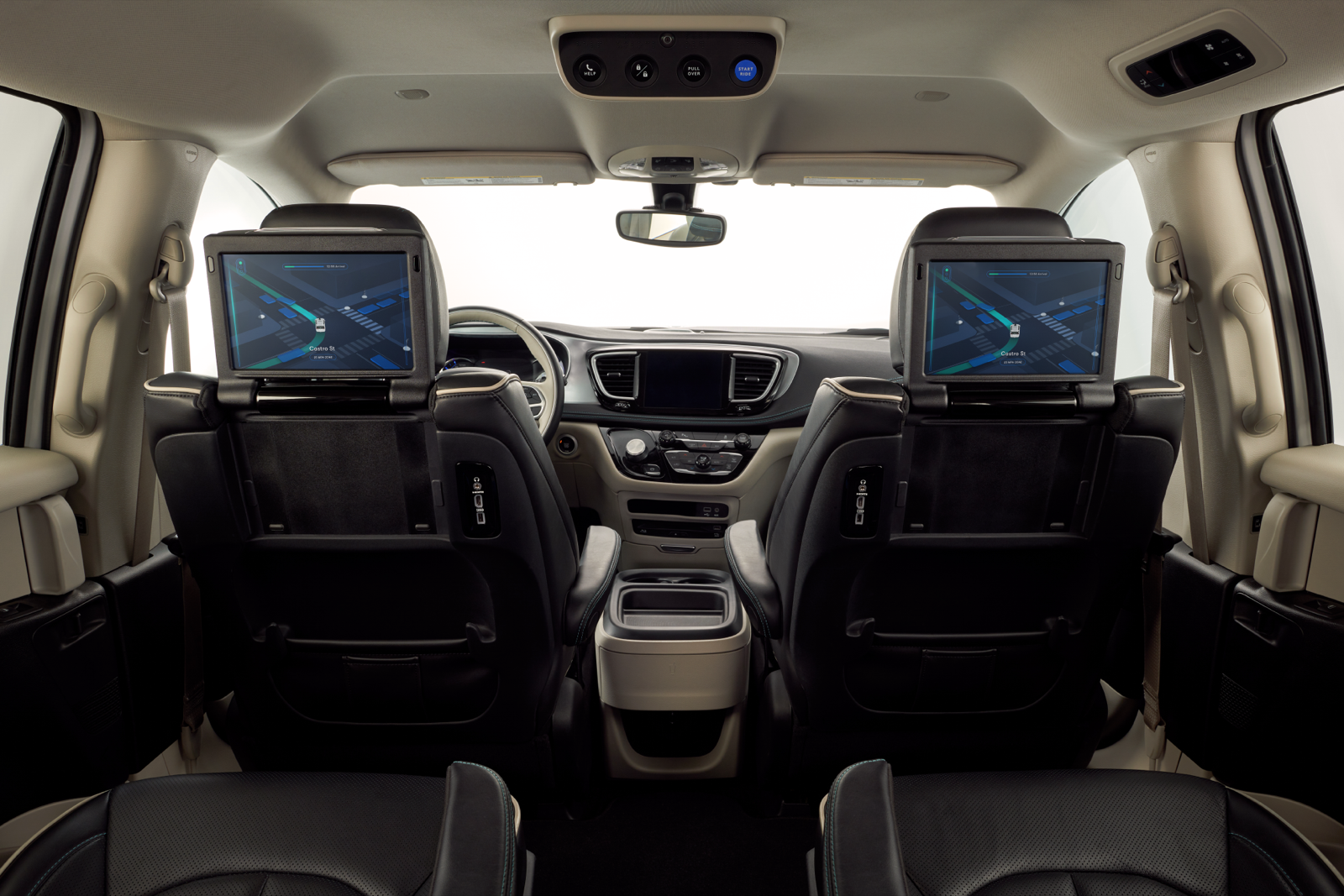
More than five years ago, a newly minted Waymo took the wraps off of what would become its first commercialized autonomous vehicle: a Chrysler Pacifica Hybrid minivan loaded with sensors and software.
Now, the minivan, a symbol of the early and hypey AV days, is headed for retirement as Waymo transitions its fleet to the all-electric Jaguar I-Pace vehicles equipped with its fifth-generation self-driving system.
When the Chrysler Pacifica Hybrid AV was first revealed, it might not have been what people expected from the former Google self-driving project turned Alphabet-owned business. The design wasn’t ripped from the pages of a graphic sci-fi novel and it was hardly flashy. But the white minivan — highlighted with the same blue and green accent colors found on the Waymo logo — embodied the company’s aim. Waymo wanted a friendly looking vehicle people would feel comfortable using.
The partnership with established manufacturer Fiat Chrysler — now Stellantis — also derisked an already risky frontier tech pursuit. Under the deal, Fiat Chrysler would handle the manufacturing and provide Waymo with minivans that built in redundancies designed for autonomous driving.
Waymo never got close to the 62,000-minivan order it agreed to in 2018 as part of an expanded partnership with Fiat Chrysler. But the minivan did become a critical part of its commercialization plan and over its lifespan the fleet provided tens of thousands of rides with the public, according to the company. (Waymo has never revealed detailed figures of its minivan fleet beyond that its total global fleet is somewhere around 700 vehicles.)
“It’s bittersweet to see it go,” said Chris Ludwick, product management director at Waymo who has been at the company since 2012, told TechCrunch. “But I’m also happy for this next chapter.”
A bit of history
Waymo revealed the Chrysler Pacifica Hybrid in December 2016 and then provided more technical and business model details a month later at the 2017 North American International Auto Show. The first look at the minivan in December came just five days after Google’s self-driving project officially announced that it was a business with a new name and slightly tweaked mission.
At the time, little was known about what the Google self-driving project — also known as Chauffeur — intended to do beyond a stated goal to commercialize self-driving cars. The Google self-driving project had developed a custom low speed vehicle without a steering wheel called the Firefly, but that cute gumdrop-shaped car never made it to commercial robotaxi status.
The lowly minivan seemed to represent a more grounded realistic vision towards the goal. By spring 2017, the company had launched an early rider program that let real people in the Phoenix area (who had been vetted and signed an NDA) use an app to hail a self-driving Chrysler Pacifica minivan with a human safety operator behind the wheel.
Waymo eventually opened up the service to the public — no NDA required — and grew its service area to Phoenix suburbs Chandler, Tempe, Ahwatukee and Mesa. Waymo repeated that process as it took the important step of removing the human safety operator from behind the wheel, launching driverless rides in 2019 and eventually a driverless robotaxi service in 2020 that was open to the public.
Minivan proving ground
The minivan’s initial reveal represented the moment when “Chauffeur” became Waymo and less of a science project, he noted. But there was still considerable work to be done.
The Chrysler Pacifica was the ultimate commercial proving ground, according to anecdotes from Ludwick, who recounted the progress of moving from autonomous driving 10 miles in one day, then 100 miles, and then a 100 miles everyday.
For instance, the company discovered that families were far more enthusiastic to use the minivan than it assumed. The minivan also helped develop the company’s AV operations playbook, including how to park vehicles in between rides and where to locate depots for maintenance and charging.
The minivan was also became a testbed for how to operate a driverless fleet during the Covid-19 pandemic. Prior to Covid, the fleet in Phoenix was a mix of driverless vehicles and those with human safety operators behind the wheel.
“In three months we turned it fully driverless and figured out how to disinfect the vehicles between each ride,” he said.
All-electric chapter
The next chapter for Waymo is focused on its all-electric Jaguar I-Pace vehicles, which will be pulled into the service area in the Phoenix suburbs of Chandler and Tempe that the minivan covered. The Jaguar I-Pace is currently the go-to driverless vehicle for robotaxi rides in downtown Phoenix and to the Phoenix International Sky Harbor Airport. The 24/7 service runs on a five-mile stretch between downtown Phoenix and an airport shuttle stop, specifically, the 44th Street Sky Train station.
On Thursday, the White House gave a shout out to Waymo (along with other companies) for its commitment to an all-electric fleet as part of the White House EV Acceleration Challenge.
Waymo intends to deploy the all-electric Jaguar I-PACE across all of its ride-hailing service territories this spring now that the minivan has been retired. The nod to Waymo was part of a larger announcement from the Biden Administration around public and private sector investments into EVs as part of its goal of having 50% of all new vehicle sales be electric by 2030.
The next task for Waymo may be its most challenging: The company has to figure out how to grow the service, charge its all-electric fleet efficiently and eventually turn a profit.
But Ludwick believes the company is well positioned thanks, in part, to the Chyrsler Pacifica.
“When I look at what the Pacifica got us, it’s a lot,” he said, noting that the vehicle had to travel at higher speeds and make unprotected left turns.
Waymo retires its self-driving Chrysler Pacifica minivan by Kirsten Korosec originally published on TechCrunch
















 English (US) ·
English (US) ·