
Expansion of BRC-20
The use of the Bitcoin blockchain is expanding, and as part of that, a new standard called “BRC-20” has appeared. BRC-20 is a method of creating unique digital assets by associating specific information with Satoshi, the smallest unit of Bitcoin.
However, in order to understand BRC-20, it is important to first know the mechanism called “Ordinals”. The BRC-20 utilizes the Ordinals protocol, enabling the creation of digital assets with greater functionality and flexibility.
In this article, we will explain the basic concepts of this new standard, BRC-20 and Ordinals, and how it will affect the Bitcoin blockchain. It also covers the challenges and ongoing debates that may arise from the introduction of new standards. Find out how BRC-20 is impacting the Bitcoin blockchain and how it might affect investors.
What is Ordinals
Ordinals is a protocol designed by former Bitcoin Core contributor Casey Rodarmor and introduced in January 2023. A system that assigns a unique number to Satoshi, the smallest unit of Bitcoin, associates Satoshi with specific information (e.g. images, videos, text formats), and tracks them. This creates a permanent digital asset on the Bitcoin chain.
Satoshi is the smallest unit of Bitcoin (BTC), named after Bitcoin’s anonymous founder Satoshi Nakamoto. 1 BTC is divided into 100 million Satoshi, and 1 Satoshi is worth 0.00000001 BTC.
connection:Biggest 4MB Bitcoin NFT Ever Minted, Community Controversial
What is Inscription
Inscription is the process used by Ordinals and BRC-20 to describe a JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) formatted text file in the witness field of a Bitcoin transaction. This makes it possible to associate token data with each Satoshi and describe it.
What is Witness Field
A concept introduced as part of a technique called Segregated Witness (SegWit). A specific field that contains additional data related to the transaction.
 Cryptocurrency Glossary
Cryptocurrency Glossary
“Engraved” Satoshi can be handled in the same way as regular Bitcoin. This means it can be sent and received in transactions and stored at Bitcoin addresses.
However, certain rules must be followed when sending these special satoshis: the Ordinals protocol. This will allow us to track in which transactions the special Satoshi was used and in what order it was moved. This is to confirm its movement on the Bitcoin blockchain while maintaining the unique information that Satoshi has.
Wallets such as at such as “ord.io” can be seen in the list of newly arrived Ordinals in Ordinals Explorer. On each Ordinals detail page, you can also see the corresponding images and videos, along with important metadata information (e.g. Name, Type, Specific Satoshi, Rarity, ID, etc.).
Difference between Ordinals and NFTs
Both Ordinals and NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) are mechanisms for creating digital assets, but the difference lies in the blockchain used and the method of creation.
NFTs are mostly created on smart contract platforms such as Ethereum (ETH), Solana (SOL), BNB Chain, etc., and use specific token standards like ERC-721 and ERC-1155 to create NFTs. . In addition, data such as the content and art represented by NFTs will be hosted on platforms such as IPFS, which are external to the blockchain.
Ordinals, on the other hand, use Bitcoin Witness Fields to directly “Inscription” basic metadata about NFTs, such as name, description, owner information, and arbitrary data such as JPEG files. Ordinals are claimed to inherit the security of the Bitcoin blockchain, albeit with a maximum limit of 40 bytes per satoshi.
What is BRC-20?
Updated the gitbook to address common questions and my intentions for the experiment going forward. https://t.co/h6fksQ1oAe
—domo (@domodata) March 10, 2023
BRC-20 is an “experimental token standard” for Bitcoin announced on March 8, 2023 by pseudonymous on-chain data developer Domo (@domodata). Although the name comes from the Ethereum token standard “ERC-20”, it does not have smart contract functionality.
The function of BRC-20 is that Satoshi, the smallest unit of Bitcoin, can be inscribed with specific data to create a unique digital asset. This mechanism uses a framework similar to Ordinals.
The Ordinals and BRC-20 tokens are a by-product made possible by the 2017 scaling proposal Segregated Witness (SegWit) and the technology introduced in the November 2021 Taproot upgrade. The original purpose of the Taproot upgrade is to introduce smart contract functions to Bitcoin, improve privacy functions and processing speed.
Difference between BRC-20 and ERC-20
The main difference between BRC-20 and ERC-20 is that BRC-20 does not have smart contract functionality. In other words, BRC-20 tokens cannot perform complex logic or functions like ERC-20 tokens. Therefore, receiving and sending tokens requires work using dedicated interfaces and tools.
Smart contracts can define and automatically fulfill contract terms. In ERC-20, operations such as transfers, checking balances, authorizing payments, and viewing total supply are managed using smart contracts, which can be interconnected with other contracts and used in dApps (decentralized apps). It will be possible.
Since there is no smart contract, BRC-20 requires each wallet to manage these tasks individually.
For example, wallets such as Unisat are responsible for “indexing” BRC-20 tokens. It knows when new tokens are created and knows exactly how many tokens a user has.
Specifically, when a token is created, that information is recorded in a Bitcoin transaction. Unisat reads that information to figure out which tokens exist, how many, and who they belong to. This will allow users to see how many BRC-20 tokens they have.
This is due to the characteristics of Bitcoin, which does not have smart contracts, and the wallet manually performs the aggregation work that is automatically performed with ERC-20 tokens.
BRC-20 should be understood to be still in an experimental stage in terms of its maturity and has technical limitations and challenges. In addition, the ecosystem is still in the process of being fully developed and should be approached with caution.
In April, a vulnerability in the code was exploited at UniSat.As a result, 70 transactions were hit by double-spend attacks, causing losses for users and Unisat to compensate.backgroundthere is. Double spending refers to sending (paying) the same token twice.
However, efforts are underway to overcome such challenges, and progress is being made in developing a trading market for the BRC-20. In May, major overseas cryptocurrency exchanges OKX and UniSat jointly announced a partnership to develop a verification process for the creation of the BRC-20 index.
connection:Major Exchange OKX Partners with Unisat to Establish Trading Environment for Bitcoin Token Standard “BRC-20”
BRC-20 issuance/trading method
Platforms such as Unisat and Ordinal Wallet are launching underlying systems to support the trading of BRC-20 tokens. In particular, Unisat is a pioneer in this field, offering users wallets supporting BRC-20 tokens. Here is a brief introduction to the main features of Unisat.
1. Create a Unisat Wallet: First, go to the Unisat website and create an account. After creating an account, create a Unisat wallet. This is where the user’s token management is based.
2. Issue BRC-20 Tokens: Next, log into your Unisat wallet and select Issue Tokens. Enter the necessary information (token name, symbol, total supply, etc.) here and issue the token. This token is created according to the BRC-20 standard.
3. Buy/Sell Tokens: Go to the trading screen within your Unisat wallet and select the BRC-20 token you wish to buy or sell. Create a buy/sell order by entering the quantity and price you want to sell. If another user has placed a matching order, the deal will go through and the token will be bought or sold.
4. Send and receive tokens: Send and receive BRC-20 tokens to and from other users using the send and receive screen within the Unisat wallet. Send tokens by specifying the destination address and the quantity to send. When receiving tokens, use the address provided by the sender.
UniSat Marketplace is Open! pic.twitter.com/WEGqGDLq4U
pic.twitter.com/WEGqGDLq4U
— UniSat Wallet – Store, Inscribe and Search. (@unisat_wallet) April 27, 2023
Unisat is a non-custodial service, meaning users are responsible for managing their own tokens and private keys. Unisat makes it easy to issue, sell, send and receive BRC-20 tokens. The operation within the wallet is intuitive, just follow the steps to manage and trade tokens.
BRC-20 token market size
BRC-20 token issuance has grown rapidly since it began in March 2023, with over 300,000 Ordinals being created in a single day at peak times.
ORDI, the first BRC-20 token, surged in value when it began trading on overseas cryptocurrency exchange Gate.io on May 8. In the past month, it has increased 190 times, reaching a market capitalization of about 54 billion yen (about $ 400 million).
After that, tokens such as NALS, UTXO, and ELON appeared, and the asset value skyrocketed from 10x to 100x. This has further fueled the memecoin craze in the Bitcoin market.
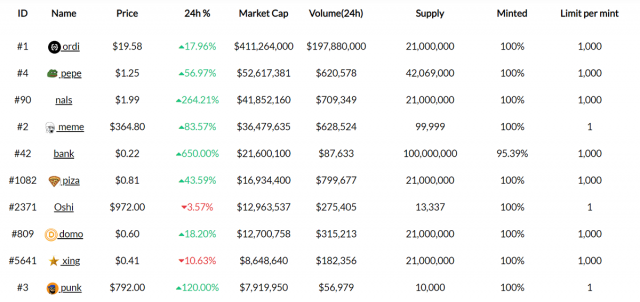
Source: brc-20.io
As of May 10, 2023, according to brc-20.io, over 14,000 BRC-20 tokens have been generated, with a total market capitalization of approximately ¥90 billion (approximately $700 million).
However, the BRC-20 trading market has low liquidity and many technical issues, so investors are required to make careful judgments and manage risks.
In addition, since there is no ecosystem such as DeFi (decentralized finance), the lack of utility in tokens issued on the Bitcoin blockchain raises questions about the sustainability of asset values. I’m here.
Impact on the Bitcoin Blockchain
The issuance of the BRC-20 token has several implications for the Bitcoin blockchain. These impacts include increased transaction costs, controversy, and a growing need for scaling solutions.
The share of Ordinals (including BRC-20) in transactions on Bitcoin increased from 10% in January 2023 to 60% in May 2023. Transaction costs are rising as demand for the block space required to issue tokens increases. This is affecting the Bitcoin remittance environment on the Bitcoin blockchain.
connection:Bitcoin remittance clogging becomes serious, Ethereum foundation sells ETH
According to data from BitInfoCharts, on May 8, the average transaction fee on the Bitcoin network soared to the $20-30 range (3,000-4,000 yen), the highest level since May 2021. Until last week, Bitcoin’s average transaction fee was about 1/10.
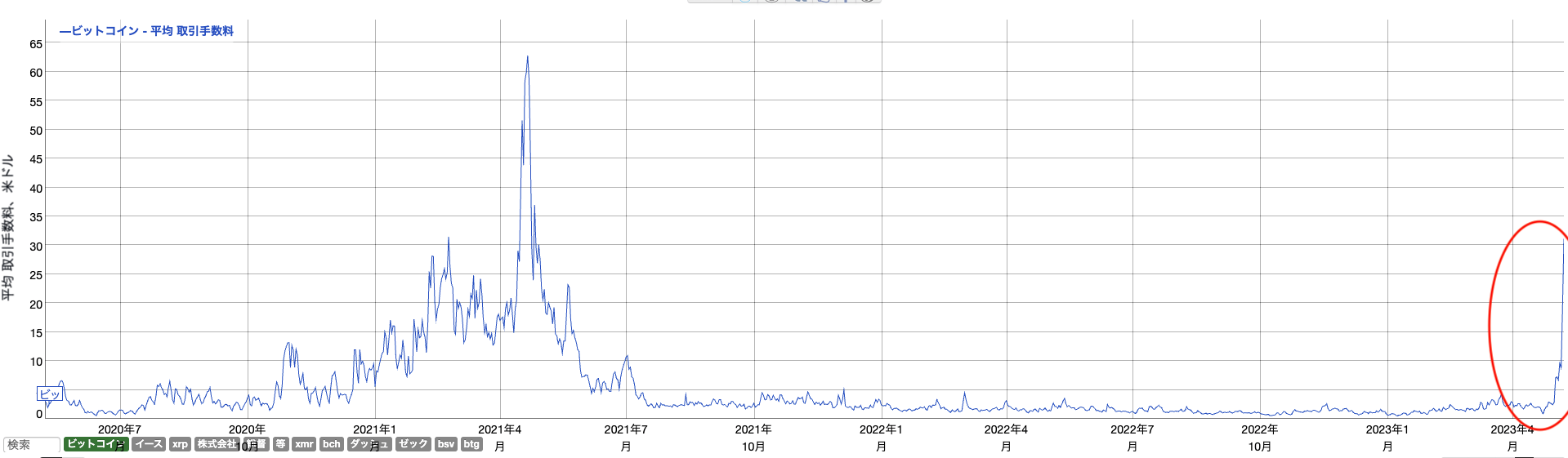
bitinfo charts
During the same period, up to about 500,000 unconfirmed Bitcoin transactions were accumulated within the memory pool. As a result, transactions of users who did not pay high fees were stuck in the memory pool, and it took a long time to be approved.
BRC-20 tokens and Ordinals have also sparked debate about how to use the Bitcoin blockchain. Some argue that Bitcoin’s mission is to be a store of value, etc., and token creation and trading should be done on sidechains or layer-2 solutions such as RGB or the Lightning Network. increase.
As BRC-20 token activity increases, so does the need for scaling solutions. As the volume of transactions grows, the blockchain’s ability to process them all efficiently becomes limited. This makes layer 2 solutions and scaling solutions like sidechains more important.
The Bitcoin developer community has proposed removing the Ordinals and BRC-20 tokens from the blockchain. We propose to remove these tokens by introducing a runtime option that disables Taproot transactions.
Bitcoin Core developer Ari Sheriff suggested adding an option to disable all non-standard Taproot transactions. This will remove these tokens from the blockchain, including Ordinals and BRC-20 tokens.
Bitcoin Core developer Luke Dash Jr. also supported the proposal. He suggested using script code such as OP_RETURN to override these transaction outputs. He also said he doesn’t want to wait for a big release as he “sees this as a bug fix”.
While this proposal is still in the discussion stage, it could have a significant impact on the future of Ordinals and BRC-20 tokens on the Bitcoin blockchain.
These tokens may be removed from the blockchain once the proposal is implemented. However, whether or not these proposals translate into the actual code of Bitcoin will depend on the consensus of the entire community.
The post What is BRC-20?Possibilities and Challenges of Bitcoin Token Standard appeared first on Our Bitcoin News.

 2 years ago
135
2 years ago
135














 English (US) ·
English (US) ·