
First upgrade after merge
The crypto asset (virtual currency) Ethereum (ETH) is preparing to implement the next upgrade “Shanghai” from March to April 2023.
The “Shanghai” upgrade includes several improvement proposals to improve the development environment, but the main purpose is to unlock the withdrawal function of validators.
Following the last upgrade, “The Merge,” which was completed in September 2022, the Ethereum network’s consensus algorithm has moved from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS).
connection:Ethereum large-scale upgrade “Merge” implementation completed
In a PoS network, instead of traditional miners, block generators are elected among validators who stake (lock up) tokens. Validators validate transactions and receive rewards in return for producing blocks.
In the case of Ethereum, each validator stakes 32 ETH and is rewarded with an annual interest rate of 4% to 6%. However, you will not be able to end staking or withdraw rewards until the Shanghai upgrade is complete.
According to the official website, as of February 17, Ethereum had 516,000 validators, and 16.5 million ETH (approximately 3.5 trillion yen), or 13.85% of the ETH supply, was locked in staking contracts. . Approximately 1.03 million ETH has been accumulated as validator rewards.
Since these ETHs can be released to the market for the first time, many cryptocurrency market participants are paying attention. In this article, we will summarize the overview of the “Shanghai Upgrade” and the opinions of each company, focusing on the withdrawal function of Ethereum.
Features implemented in the Shanghai upgrade
In the media, it is often abbreviated as “Shanghai”, but strictly speaking, the next upgrade is called “Shanghai-Capella”. Ethereum consists of an execution layer (EL) and a consensus layer (CL). Shanghai refers to upgrading the execution layer, and Capella refers to upgrading other consensus layers.
Of these, the EIPs (Ethereum Improvement Proposals) included on the Shanghai side are the following five points. Other than the implementation of the withdrawal function, all of them are aimed at reducing the gas fee paid by developers and validators.
- EIP-3651: Implementation of “Warm COINBASE”, lower gas cost for validators
- EIP-3855: Writing “Push0” Code to Reduce Gas Costs for Developers
- EIP-3860: Put Gas Caps in Code Developers Use for Smart Contracts
- EIP-4895: Introduce withdrawal functionality to staking
- EIP-6049: Mechanism for Notifying Developers of Code Depreciation “SELFDESTRUCT”
On the other hand, implementing Capella upgrades in the consensus layer (CL) allows interaction with EL. Validators lock ETH on CL, and when they are completely withdrawn, a withdrawal request (queue) is issued from CL to EL. Strictly speaking, there are two types of withdrawal requests, each of which affects the number of days until the ETH withdrawal is completed, but the details will be described later.
Schedule until Shanghai implementation
On February 8, 2022, “Shanghai (Capella)” was successfully launched on the Ethereum public testnet Zhejiang (Zhejiang Province). On the testnet, service providers such as cryptocurrency exchanges and staking pools will check the staking ETH withdrawal process before going live.
After Zhejiang, we plan to launch Shanghai with two more public testnets. According to core developer Tim Beiko, Sepolia will implement Shanghai on February 28 first, and will also roll out to the Goerli testnet by mid-March. Although not officially announced, according to Ethereum News, the Shanghai implementation in production could be launched a few weeks after Goerli (around the end of March/April).
connection:Ethereum Set Next Test Of Shanghai Upgrade To End Of February
Staking ETH withdrawal process
Ethereum has a withdrawal limit to prevent a large number of validators from leaving at once and becoming unstable. According to the ETH Withdrawals FAQ, there are two options, each with a different waiting period for withdrawals.
- Method 1, “Partial Withdrawal” to unstake only the accumulated rewards earned from validators
- Method 2: “Withdraw all” to end the validator and unstake all 32 ETH + accumulated rewards
In addition, there are “withdrawal queues” and “exit queues” for withdrawal requests. In the case of partial withdrawals, only the withdrawal queue is processed by the net withdrawal method, and the average withdrawal period is 4.5 days.
On the other hand, in the case of (2) “withdrawal in full”, the withdrawal queue is first put out, and after passing through, it takes a day to a little more than a month to wait. Since more exit queues will be issued after this waiting time has elapsed, it will be necessary to wait additionally if many exit queues are rushing at that time.
In the current design, the withdrawal queue is a specification that allows up to 16 validators with one slot (≒ block) every 12 seconds.
Full withdrawal process
When a validator wants to withdraw from Ethereum, it must 1) pass through the exit queue and 2) pass a waiting period.
The traversable withdrawal queue per epoch (~6.4 minutes) is limited to 7 validators (at time of writing*). 225 epochs per day allows 1,575 validators to pass through the withdrawal queue, which is 50,400 ETH (32 ETH x 1,575) minutes. *As the number of validators increases, the number of withdrawal requests per epoch also increases.
If the withdrawal queue is crowded, validators will have to wait their turn. During this time, validators must continue to perform their duties.
Also, when the validator withdrawal queue passes, there will be a waiting period of 256 epochs (about 27 hours), which will be extended to 8,192 epochs (up to 36 days) if you have been penalized in the past. After this waiting period, withdrawal queues can be placed.
 Cryptocurrency Glossary
Cryptocurrency Glossary
Staking ETH Withdrawals and Selling Pressure
With the ability to withdraw staked ETH, there is growing interest in how it will affect supply and demand in the ETH trading market.
The first liquidity ETH is supposed to be a “partial withdrawal” that unstakes only the cumulative rewards earned by validators. Since the surplus exceeding 32 ETH does not generate rewards, it will be withdrawn and sold or staked again.
Major U.S. cryptocurrency exchange Coinbase reported that 640,000 ETH (67%) of the accumulated rewards (approximately 1.03 million ETH) distributed to 516,000 validators were staked by intermediary services such as Lido. assumed to be used for adding staking. We expect 340,000 ETH (70 billion yen) to be sold for the time being.
In addition, Coinbase points out that withdrawals of 350,000 ETH to 1.145 million ETH will occur from the Kraken exchange in the United States. Kraken must cease its staking service in the United States as part of its settlement with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Kraken currently accounts for about 7% of the total staked ETH (1.23 million ETH), but considering that there are a significant number of non-US users, and some US users will re-stake on other services. I did.
Based on the above, the maximum staking ETH withdrawal demand is estimated to be 1,145,000 ETH + 340,000 ETH. 13.8 billion yen), Coinbase estimates.
Meanwhile, ETH’s daily trading volume has averaged $8.2 billion (1 trillion yen) over the past 30 days (data: analytics firm TIE). As such, Coinbase argued that the ¥13.8 billion sale would be “easily absorbed by the market.”
A similar view has been expressed by Galaxy Digital, a major US cryptocurrency investment firm. Galaxy believes that up to 50% of the ETH from the unlocked rewards will be sold, as the price of Ethereum is below the price at which many validators acquired ETH.
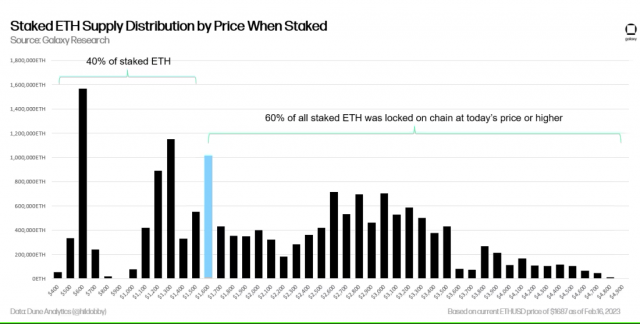
Source: Galaxy Digital
Galaxy Digital also assumes that 100% of the ETH of the 1,138 validators that have already stopped working and will almost certainly withdraw will be sold, while “there is no reason for Kraken users to sell.” .
In conclusion, Galaxy said that the total sales volume for the seven days after Shanghai totaled 553,650 ETH, or about 1% of the weekly ETH volume (including physical and perpetual futures).
According to the on-chain analysis company glassnode, the average acquisition price of staked ETH was $2,404 (approximately 300,000 yen) as of July 2022. There is some persuasiveness in Galaxsy’s view that it is unlikely that the company will be sold.
With the price declines over the weekend, the #Ethereum market has fallen below the $ETH Realized Price of $1,781.
This means the market is holding an average unrealized loss of -18.4%
The Realized Price of ETH 2.0 deposits is higher at $2,404, with an unrealized loss of -39.6% pic.twitter.com/yleNe7111X
—glassnode (@glassnode) June 12, 2022
connection:What impact will the Shanghai upgrade scheduled for March have on the Ethereum market?
Shanghai Upgrade Fuels ETH Demand
Even if the Shanghai upgrade causes some short-term selling pressure, many operators expect it to lead to increased demand in the medium- to long-term. This is because investors who have been concerned about the lack of withdrawal functions may start staking new ETH.
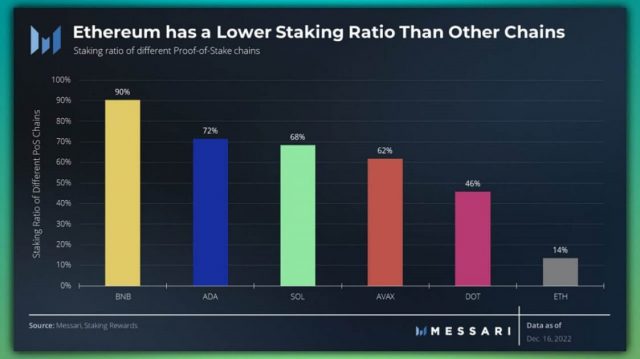
Source: Messari
According to data from analytics firm Messari, the staking share of Ethereum (ETH) supply is 14%, the lowest among other Layer 1 blockchains. With an average of 65% and 90% for BNB, there is still room for expansion.
Matt Hougan, chief investment officer at crypto index fund manager Bitwise Asset Management, said, “If the (de facto) indefinite lock-up is lifted, the proportion of investors seeking ETH staking will drop. Explosive growth”, predicting that the staking rate of ETH in circulation will increase by at least 50% by the end of 2023.
Investment bank JP Morgan points out that 95% of Coinbase’s retail investors may participate in Ethereum staking after the Shanghai upgrade, and Coinbase’s annual revenue is now 225 million. It is estimated that it will expand from US$ (29.5 billion yen) to US$545 million (70 billion yen).
connection:US Coinbase: Ethereum selling pressure after Shanghai upgrade is limited
The post What is the ETH “Shanghai” upgrade?Summary of each company’s view on staking cancellation and ETH selling pressure appeared first on Our Bitcoin News.

 2 years ago
191
2 years ago
191














 English (US) ·
English (US) ·