
Plan to utilize ZK-SNARKs
Ethereum (ETH) co-founder Vitalik Buterin published a new proposal for integrating ZK-EVM into Ethereum Layer 1 (L1) on his blog on the 14th. This proposal has the potential to significantly improve Ethereum’s efficiency and security.
According to Buterin, in the future, the light client is expected to have enhanced functionality, making it possible to leverage ZK-SNARKs to fully verify the execution of the Ethereum network’s Layer 1 EVM. As a result, a de facto ZK-EVM (Zero Knowledge Proof Ethereum Virtual Machine) exists on the Ethereum network, and consideration is required to make maximum use of it.
What is zk-SNARKs?
“zk-SNARKs” are zero-knowledge proofs. A type of proof protocol, a mechanism in which the prover proves that a claim is true without disclosing any information other than that the prover’s claim is true to the verifier.
 Virtual currency glossary
Virtual currency glossary
L2 structural issues
Buterin details the challenges facing Layer 2 EVM protocols on Ethereum, specifically Optimistic Rollups (OP Rollups) and ZK Rollups (ZK Rollups).
These protocols replicate the EVM functionality present in the Ethereum protocol, among them the (L2) ZK-EVM, which features EVM equivalence, which is essentially a Layer 1 (L1) of the Ethereum block. The situation is that we are performing the same work as verification. In other words, if there is an update to L1, there is a need for governance on the L2 side to follow it.
However, according to Buterin, Ethereum’s Layer 1 directly providing ZK-EVM could significantly reduce the need for governance at Layer 2, thereby increasing Layer 2 efficiency and security. There is.
What is rollup and ZK-EVM?
Rollups that are expected to solve Ethereum’s scalability problems can be divided into two types: Optimistic Rollups and Sozk Rollups that utilize zero-knowledge proofs. Typical examples of ORs are “Optimism” and “Arbitrum.” ZK-EVMs include “zkSync,” “Scroll,” and “StarkNet.”
 Virtual currency glossary
Virtual currency glossary
connection:What is layer 2 of blockchain? Explaining types, points of interest, and typical networks
Basic structure of “Enshrined ZK-EVM”
Dubbed “Enshrined ZK-EVM,” the plan calls for massive parallelism and “recursive SNARKs” to reduce the computational resources and time currently required to generate proofs for Ethereum blocks. It is proposed to use This makes it possible to efficiently integrate multiple proofs and improve the efficiency of the entire process.
Additionally, new transaction types similar to EIP-4844’s “blob” transactions (such as ZKEVMClaimTransaction) are introduced to streamline data transfer in the L1 Mempool. This includes a ZK-SNARK that certifies the correctness of the relevant transaction and witness data.
connection:What are the importance and benefits of Ethereum’s next upgrade “Dencun”, EIP-4844?
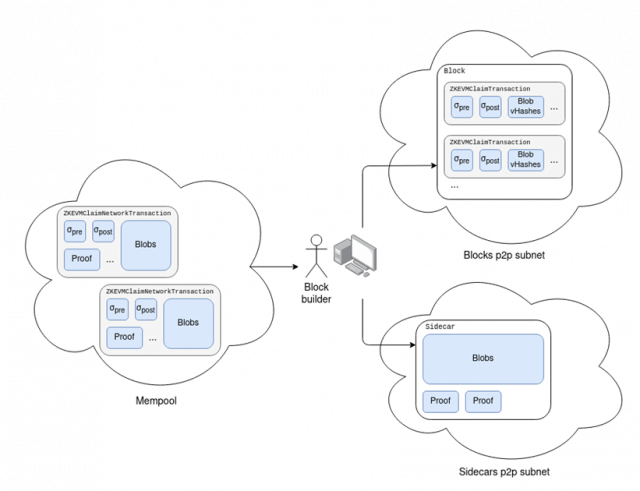
The “sidecar” that stores additional information associated with block data in the client’s local environment is split into two parts: one for “blobs” (temporary large data packets) and one for “sidecars” that store additional information associated with block data. Use it for “proof”. Create separate subnets (separate areas within the network) for each type of certification. Source: notes.ethereum.org
Additionally, new verification rules will be introduced at the consensus layer (part of the blockchain consensus building process). With this rule, the client verifies a valid proof (ZK-SNARK) for each claim in the block.
Clients can withhold confirmation of a block until they have a minimum of M of the required N proofs, and this process maintains the integrity of the blockchain network and prevents fraudulent activity due to malicious activity or errors. This is important to prevent block approval.
connection:What is StarkNet? Explaining why it is attracting attention as layer 2 of zk rollup and the development plan
Role of L2 project
Currently, the L2 project is responsible for block validation and transaction processing to improve Ethereum’s scalability and efficiency.According to Buterin’s proposal, with the integration of ZK-EVM, the L2 project will continue to have many important functions.
For example, since the speed of L1 slots (related to block generation) may be delayed, the L2 project is expected to improve the user experience by providing quick advance confirmation.
These projects will also serve to extend EVM to provide new approaches like Arbitrum Stylus’ WASM support and the Cairo language, further increasing the efficiency and scalability of the Ethereum ecosystem.
connection:“Ethereum expected to outperform Bitcoin’s growth rate” JP Morgan predicts next year
Assignment details
Buterin’s proposal considers options and tradeoffs for multi-client systems. A multi-client system is a system in which different clients (software) run the same blockchain protocol.
It is important to strike a balance between closed and open systems, including existing ZK-EVMs (PSE ZK-EVM, Polygon ZK-EVM, Kakaro, etc.), so that network security and efficiency can be maintained while maintaining , is said to be able to promote flexibility and innovation.
Additionally, issues related to ZK-EVM, such as auditability and upgradability, have been raised. Overcoming these challenges is expected to improve the security and reliability of the Ethereum blockchain and open new avenues for blockchain technology.
connection:What is layer 2 of blockchain? Explaining types, points of interest, and typical networks
The post What is the evolution of the virtual currency Ethereum, Mr. Buterin’s ZK-EVM integration proposal and the future of Layer 2? appeared first on Our Bitcoin News.

 1 year ago
95
1 year ago
95














 English (US) ·
English (US) ·